
Types of solar panels
Types of solar panels
What types are there? Which one is the best one for you?

Reading time: 6 min
Agrivoltaics
Contributing to achieving a sustainable primary sector
Thanks to the combined use of land for energy generation and agricultural or livestock production, agrivoltaics or agrivoltaic energy is becoming an essential tool for advancing toward "smart farming" and for offsetting the consequences of climate change.
Is it possible to implement a highly efficient production model in the agricultural sector without harming the environment? Without a doubt, this is one of the major challenges facing businesses in the sector today. To achieve this, investment in R&D&I focuses on the development of new green and efficient technologies as well as in innovative ways of applying them, such as agrivoltaics, an excellent example of sustainable economy based on the synergy between agriculture and photovoltaic solar energy.
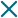

What is agrivoltaics?
Agrivoltaics represents an innovative way to minimize the effects associated with the primary sector as they increase the efficiency of crops and reduce their environmental impact, among many other benefits.
Water consumption, the emission of polluting gases, and the use of fertilizers and plant protection products (pesticides, herbicides, etc.) that are harmful to nature are some of the primary environmental risks associated with the farming sector.
The idea of combining different types of renewable energy with agriculture was first conceived in 1981 by the Germans Armin Zastrow and Adolf Goetzberger, the founder of the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE. However, the concept of agrivoltaics didn't really become popular until the past decade thanks to performance studies carried out by the Frenchman Christophe Dupraz.
This model of sustainable agriculture, closely related to “smart farming,” consist of the installation of photovoltaic solar panels on land intended for crops or cattle. This gives the land a dual purpose: agricultural or livestock production and solar energy generation – a renewable, infinite, and eco-friendly electricity source.
In agrivoltaic structures, panels are installed on structures or cables several meters above the ground to allow access for agricultural machinery. The system can also modify the orientation of the panels to maximize their efficiency based on a mathematical model that receives data from the sensors installed on the property. It also adjusts the areas of shade depending on the meteorological conditions and needs of the different crops, thus adapting to their phases of growth.
Advantages of agrivoltaics
Uses and applications for agrivoltaics
Now that you know how it works and the benefits it offers, check out some examples of how agrivoltaics is applied today. The most common way of implementing this type of energy consists in the installation of solar panels above crops and using it in combination with the production of food products. This system is especially well adapted to dry farming (non-irrigated cultivation of crops).
Examples of agrivoltaic projects
Spain has the ideal environment for implementing agrivoltaics given its expansive farming land and climate, with nearly 2,500 hours of sunlight per year. These conditions make agrivoltaics the optimal solution for increasing the efficiency of many cultivated lands in our country. We can already find initiatives such as Repsol's, which partners with the technology company PowerfulTree at the San Gabriel Enology School vineyards, located in Aranda de Duero in the Burgos municipality.