
Wave power
Wave power
This type of energy takes advantage of the movement of waves to generate electricity. Do you want to know how?
-scr.jpg)
All about hydropower plants
Harnessing kinetic energy
What is a hydroelectric or hydropower plant?
Also known as a hydroelectric power plant, it is an infrastructure whose main purpose is to capture and exploit the kinetic energy contained in the natural flow of water.
These plants are strategically located along rivers and streams, where the powerful force of moving water becomes a fundamental resource for electricity production.
Hydropower plants generate a renewable energy source that contributes to sustainability and the reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions (GHG). In addition to mitigating the adverse effects of climate change, they are highly efficient and versatile, adapting to different scales of power generation, from microgeneration to large-scale projects, supplying entire regions with clean electricity.
How hydropower plants work
Hydropower plants employ a number of key components and an ingeniously designed process that efficiently harnesses the hydrological cycle.
Water catchment. A strategic location is chosen on a river or reservoir where a large amount of moving water can be captured. This is done by means of a dam or weir that controls the flow of water.
Water conveyance. The water is directed through a pipeline or conduction channel that guides the water to the hydropower plant.
Turbine activation. The water reaches hydraulic turbines through the pipeline, which are activated by the water flow.
Power generation. The turbines are connected to electric generators called alternators, which cause electricity to be produced when the water turns the hydraulic turbines.
Current transformation. The electricity generated in alternators is initially an alternating current (AC). This usually has a low voltage, so a transformer is used to increase its voltage and make it suitable for long-distance transmission.
Transmission and distribution. The electricity generated is transmitted over high-voltage transmission lines to the points where it is needed. Often, an electrical substation is used to reduce the voltage before distributing it to consumers.
Control and regulation. Hydropower plants are equipped with control and regulation systems that monitor and adjust water flow and electricity generation to maintain a constant and stable supply of energy.
Energy storage. Some hydropower plants have the ability to store water in a reservoir. This makes it possible to regulate water flow and electricity generation according to demand, which makes them a flexible energy source.
Types of hydropower plants
There are different types of hydropower plants depending on factors such as the availability of water resources, the scale of power generation required, and geographical conditions.
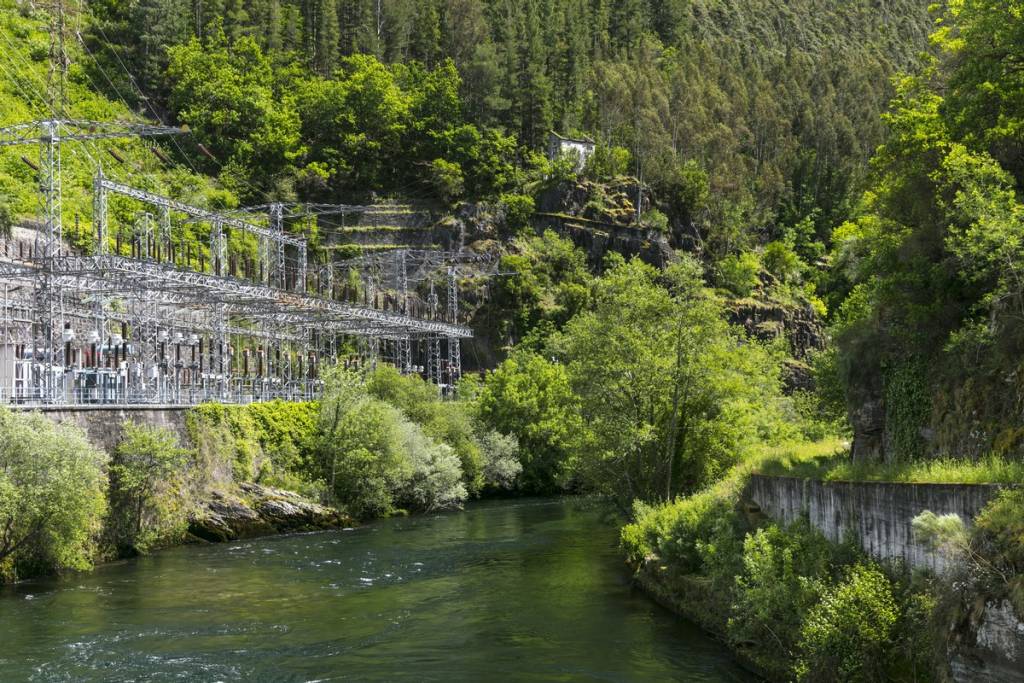

Run-of-river hydropower plants
They harness the constant flow of water from rivers or streams, without using reservoirs. The water is diverted through a channel and directed through a pipe to a turbine that generates electricity. They are especially efficient and suitable for areas with constant flows of water.
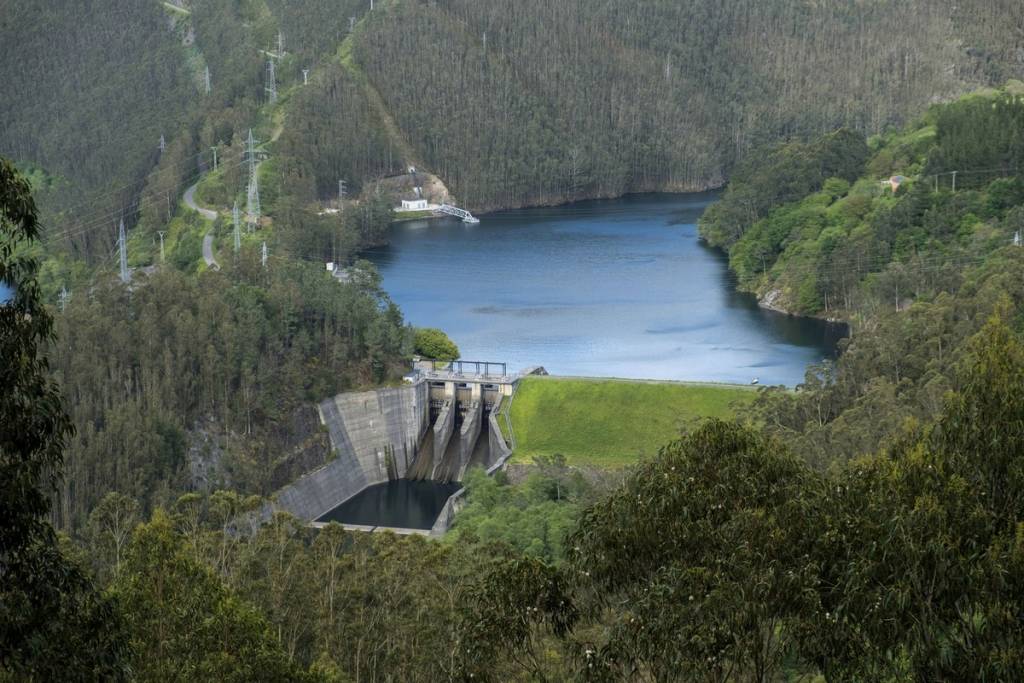

Hydropower plants with a reservoir
Water is stored in reservoirs and the flow to the turbines is regulated. They can be large scale (traditional hydropower plants), or smaller in size. Reservoirs offer flexibility to adjust electricity production according to demand.
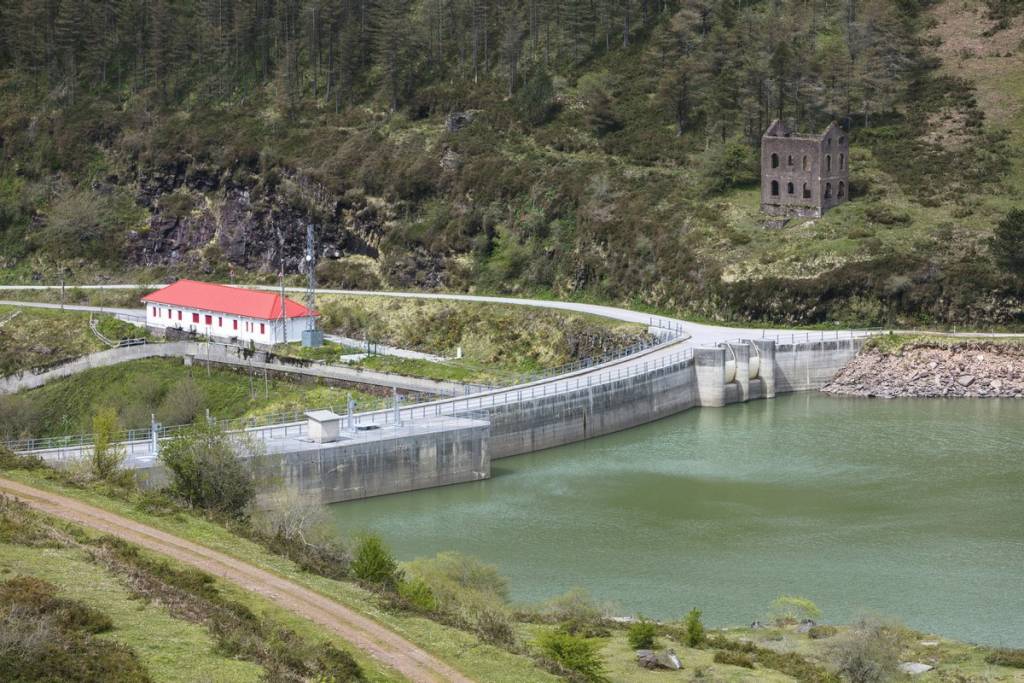

Pumped-storage hydropower plants
They are essential for storing energy. In periods of low demand they pump water from a lower reservoir to an upper reservoir using electricity. If it is high, water is released from the upper reservoir by hydraulic turbines. An example is the pumped-storage hydropower plant in Aguayo, Cantabria.

Bypass or channel hydropower plants
Instead of blocking the river with a dam, these plants divert part of the water flow through a channel to the turbines, allowing the river to continue its course. This minimizes environmental impact, although it reduces water storage capacity.
Repsol Electricity and Gas for home comfort
By contracting Repsol Electricity and Gas, in addition to saving, you will receive a host of benefits. Find out more.
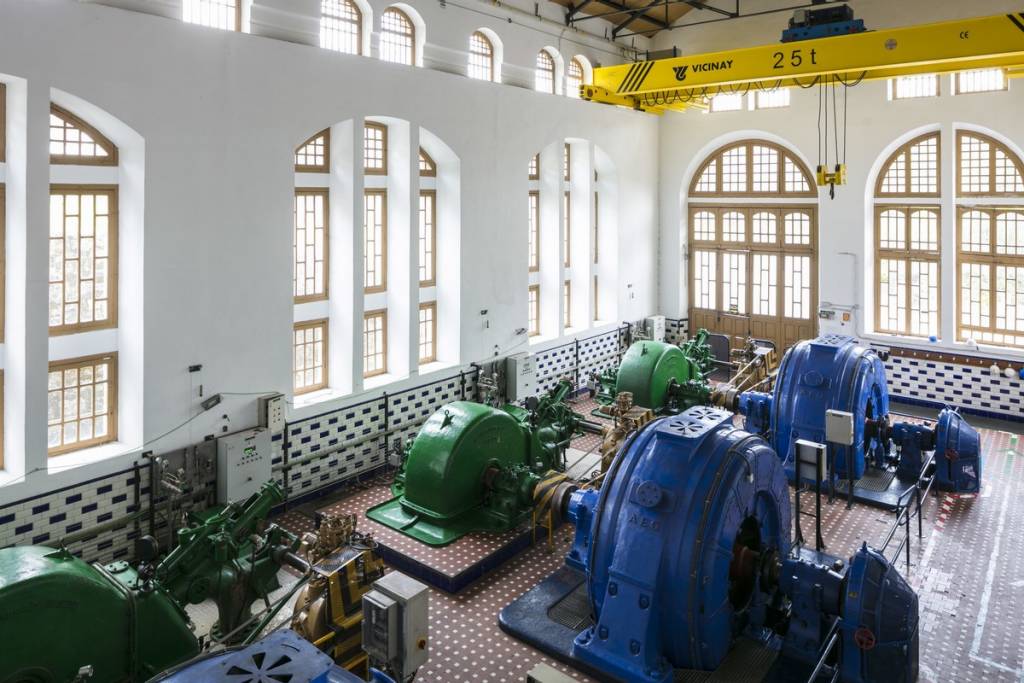
Parts of a hydroelectric power plant
Although the configuration and size of a hydroelectric power plant can vary depending on the type of location, the main parts are:
Benefits of hydraulic power plants
There are different types of hydroelectric power plants, depending on factors such as the availability of water resources, necessary generation scale, and geographical conditions.
Renewable energy source
Hydroelectric power plants use the water cycle, a renewable and environmentally friendly energy source. They do not emit polluting gases, which contributes to reducing the carbon footprint.
Flood control
Dams can help control floods by regulating water flow to rivers and streams, being an important component in power plant safety.
Energy storage
Power plants with reservoirs can store water, allowing them to adjust hydraulic energy production on demand. This makes them very useful for managing the intermittency of other renewable sources.
Grid stability
These power plants provide grid stability by supplying constant and adjustable hydraulic power, reducing the risks of blackouts and voltage fluctuations.
Long useful life
Hydroelectric power plants tend to have a long lifespan, allowing for long-term power generation with profitable initial investments.
Energy efficiency
They are highly efficient at converting kinetic energy into electricity, making them a safe energy source.
Supplying homes with hydraulic energy
You may also be interested in

Wave power
This type of energy takes advantage of the movement of waves to generate electricity. Do you want to know how?

Solar power plants
Learn about what they are, the different types, and how they work. Find out everything about these facilities.

How to save water
As a limited and indispensable resource, it is essential to save water. Here are some tips on how to do it.