
Wave power
Wave power
Discover the energy of waves.

Everything about tidal power
Making the most of the tides
What is tidal power?
Tidal power, also called ocean energy, is a type of renewable energy that is capable of making the most of the movement of tides and transforming it into electricity.
Tidal power is therefore a source of clean and endless energy, so it's a perfect option to advance towards a more sustainable energy system. Platforms such as BiMEP, the Biscay Marine Energy Platform, whose main function is the testing and demonstration of offshore wave catchers, confirms that oceans and tides can be a great ally in renewable energy.
Currently, thanks to R+D+I (research + development + innovation), renewable energy sources constitute a key piece to comply with the Paris Agreement objectives and reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. For its part, the International Energy Agency (IEA) affirms that the participation of renewables in the global electric supply “will go from 26% in 2018 to 44% in 2040”, which will also have a positive economic effect on the global economy and development.
Types of ocean energy
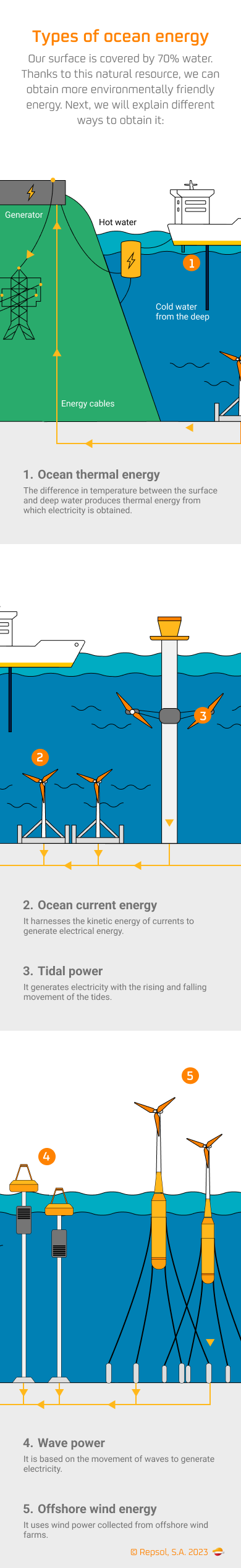
What advantages does tidal power have?
It's a renewable and clean energy
It's an endless energy source that also doesn't emit any greenhouse gas, nor needs additional fuels, so it's environmentally friendly.
It's highly predictable
Tidal cycles are easy to predict and therefore to manage. The power that each tidal power plant can offer can be known in advance, so it's a reliable electricity production system.
It's efficient at low speeds
Tides can generate electricity at very low speeds since in their case the most important thing is the high volume of the water mass and not so much the speed of its displacement.
As well as these advantages, you also have to bear in mind that tidal power plants have a very long useful life. To date, there are still few power plants of this type, but the results are very positive. For example, the first tidal power plant was built in Rance (France) in 1966, so it has been operational for more than 55 years, and it's estimated that it will be able to generate electricity for much more time. Below we'll learn in more detail how these types of power plants operate.
How does a tidal power plant work?
Tidal power plants are responsible for the process of transforming tidal power into electricity. To manage it, underwater installations that meet some very specific geographical conditions are required.
According to the IDAE, Institute for the Diversification and Saving of Energy, a tidal power plant has to be installed in an estuary, a bay, or sea inlet where the difference between the high tide (maximum sea level) and low tide (minimum sea level) is more than 5 meters. Taking these characteristics into account, tidal power plants are built with turbines and alternators that with the turn of their blades and the circulation of the water itself can produce electricity.