Characteristics of Smart Grids
Characteristics of Smart Grids
Some of the most important features of smart grids are:
Greater flexibility
Greater flexibility
The automation of processes and the application of smart systems make it possible to respond quickly to unforeseen events or incidents and provide an immediate response, even remotely.
Increased safety
Increased safety
The smart grid provides an even more reliable, efficient, safe, and sustainable electricity supply, resulting in improved service quality.
Response to demand and savings
Response to demand and savings
They allow users to connect their electronic devices at times when rates are lower. This translates into direct savings on their electricity bills.
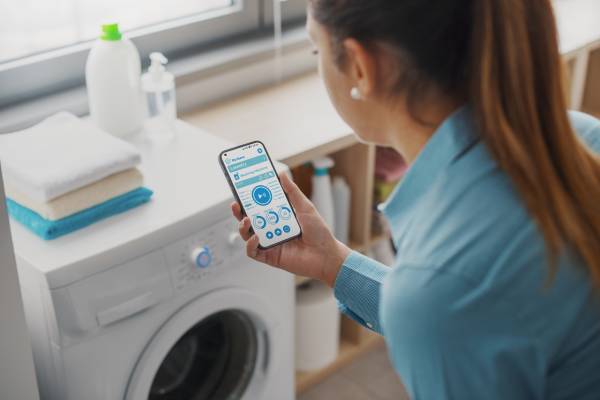
Load management
Load management
Thanks to smart grids, users can learn the electricity rate at which they are consuming energy, in real time. This makes it possible to manage and reduce use, which would avoid, for example, overloads.
Decentralization of production
Decentralization of production
Users are not only consumers, they can also generate energy. Through smart grids, surplus energy can be stored or transferred to the general power grid so that other users can take advantage of it.




