Decarbonization of the air sector
Decarbonization of the air sector
Technological advances and biofuels are bringing us increasingly closer to the decarbonization of the air sector. Discover how with Repsol.

Electrolyzer: what it is, types, and common uses
Decompose to decarbonize
Decarbonization involves the production of energy with lower emissions. In this regard, hydrogen can provide us with a large amount of versatile and non-polluting energy. Electrical, mechanical, or thermal energy can be obtained from hydrogen, with high performances and zero CO2 emissions since, once the hydrogen is burned, it only generates water vapor as a residue. Renewable hydrogen produced by electrolysis is a promising alternative in the transition to a more sustainable energy system.
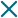

What is an electrolyzer?
An electrolyzer is a device that, through the application of electricity, can separate water molecules into its two components: hydrogen and oxygen.
The electrolyzer consists of two electrodes, an anode (or negative electrode) and a cathode (or positive electrode), which are responsible for passing the electric current through the water and carrying out the process of "breaking" the molecules, known as electrolysis.
When the electrical energy used comes from renewable sources, the process is 100% sustainable.
As we have already mentioned in the previous section, electrolysis consists of the separation of water into its elements —hydrogen and oxygen— through the application of an electric current. As well as the two electrodes (anode and cathode), a component called electrolyte is required. This can be an acid, a base, or a salt dissolved in water, and serves to facilitate electrical conduction. It was Faraday who first formulated the principle of electrolysis in 1820.
In the case of renewable hydrogen, the electricity that is applied in the process is generated from renewable sources. The hydrogen released when the water decomposes is collected and undergoes a process that removes impurities and enables it to meet the required quality standards. It is then stored in tanks or transported through pipelines for distribution.
Types of electrolyzer
Depending on their operation and size, there are currently several types of electrolyzers, among which the following stand out:
Repsol: Net zero emissions commitment by 2050
At Repsol, we have a clear objective: to be a net zero emissions company by 2050. For this purpose, we have set a roadmap with ambitious goals, the Route towards decarbonization.
Applications of renewable hydrogen
Mobility field
Hydrogen-powered fuel cell vehicles are a growing option for heavy-duty road transport. Synthetic fuels (net zero emission fuels from water and CO2) are made from renewable hydrogen.
As a raw material
It is also used as a raw material in refining processes —one more step for the decarbonization of the energy industry— or in the chemicals industry, to produce ammonia, methanol, and other chemicals.
As an energy vector, it can be produced with renewable energies during periods of low demand and then be used to generate electricity through fuel cells or hydrogen turbines.
Heating and refrigeration
Renewable hydrogen can be burned in hydrogen boilers to generate heat or even be used in absorption refrigeration systems.
Electrolyzer projects today
The commitment to renewable hydrogen generation is strong in several countries. In fact, the European Commission presented the document "A hydrogen strategy for a climate-neutral Europe" in mid-2020, and in 2022 the green light was given for the investment of 5.2 billion euros in public funding to promote hydrogen research and innovation.
At Repsol, we work alongside Petronor to promote renewable hydrogen on the Iberian Peninsula. For this reason, we are installing the first electrolyzer in the Basque Country, in Petronor's industrial complex in Muskiz. It will have a capacity of 2.5 MW and will entail an investment of 8.9 million euros.
The project will be integrated within the Basque Hydrogen Corridor (BH2C), an initiative that 80 entities have already signed up to and aims to boost economic recovery not only in the Basque Country, while making progress in the decarbonization of the energy sector. In Cartagena, it is also planned to activate an electrolyzer with a capacity of 100 MW, as part of the Green Hydrogen Initiative of the Region of Murcia, focused on the Escombreras Valley area.
However, the most ambitious project so far by Repsol will be implemented in Tarragona. It is an electrolyzer with a capacity of 150 MW by 2026 and 1,000 from 2027. This facility will have the best technologies to minimize the consumption of water destined for renewable hydrogen production.
Decarbonization of the air sector
Technological advances and biofuels are bringing us increasingly closer to the decarbonization of the air sector. Discover how with Repsol.

Renewable hydrogen in mobility
Discover the gas that will mark the future of sustainable mobility. Discover renewable hydrogen.