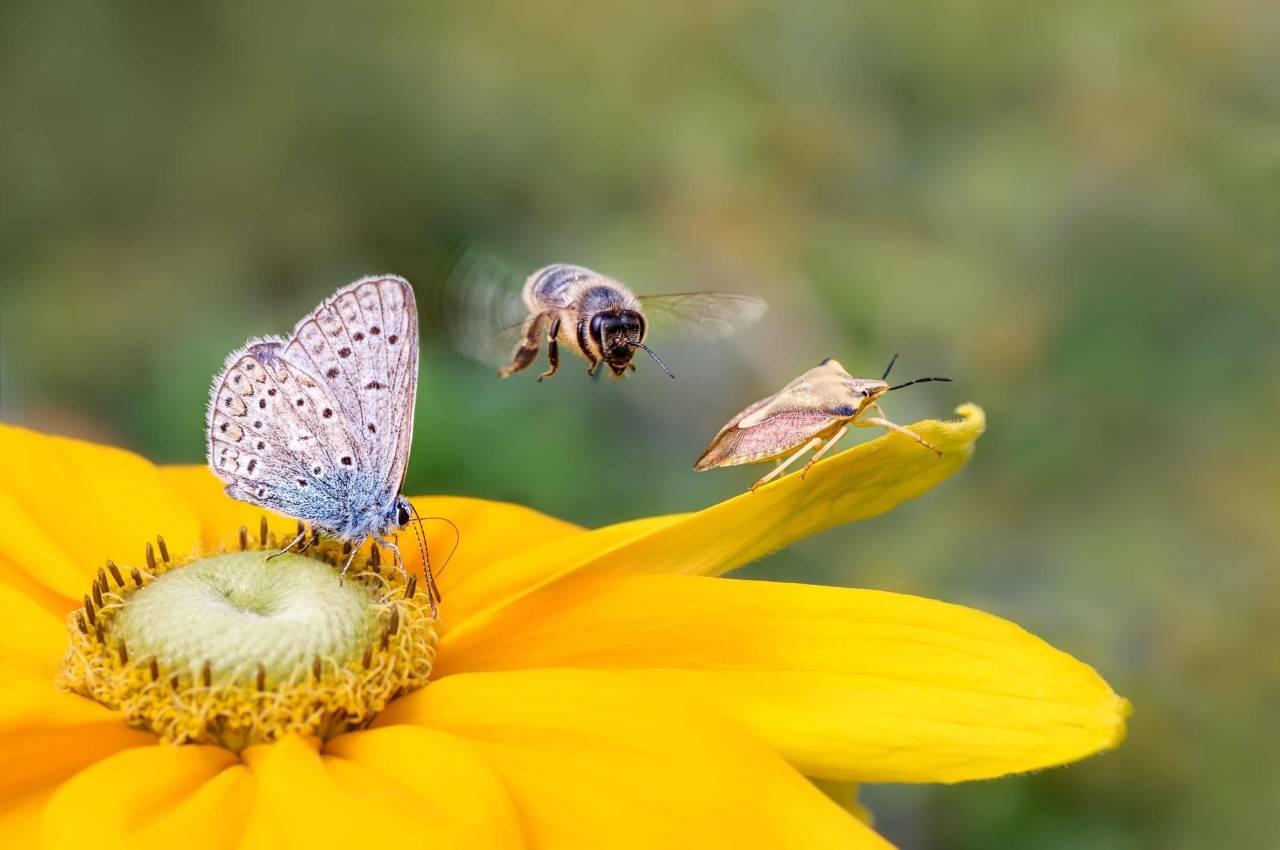
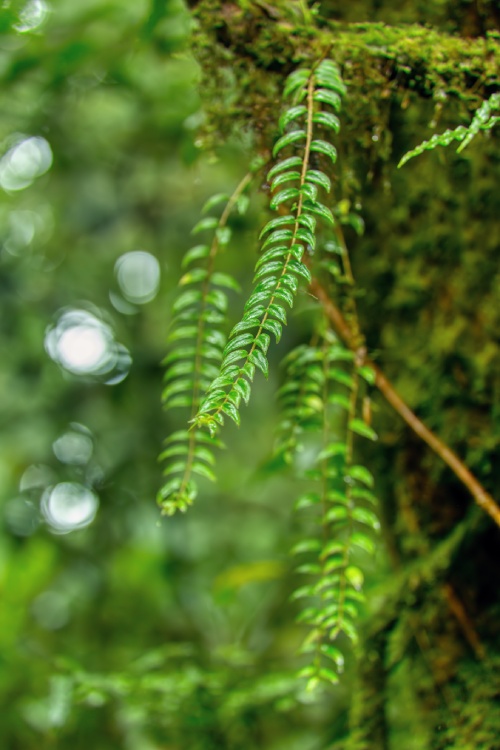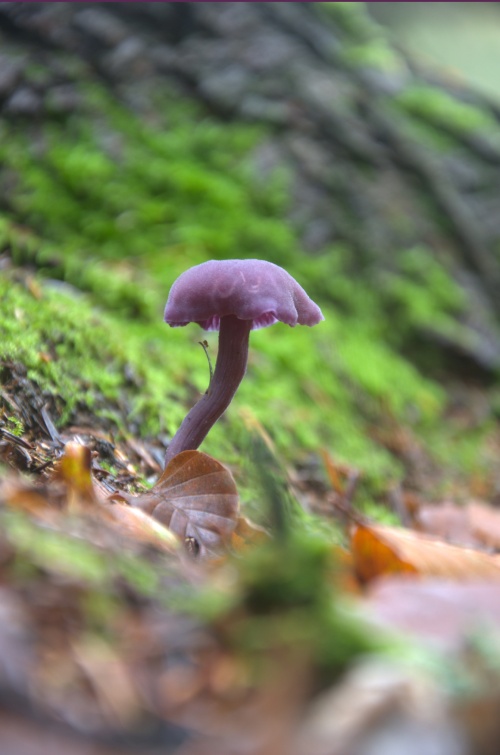
What is biodiversity?
What is biodiversity?
Seeking an ecological balance
Seeking an ecological balance
"Variety is the spice of life," as the old saying goes. And that explains why various forms of life on Earth – insects, plants, mammals, amphibians, and even microorganisms – can interact and live harmoniously. This is known as ecological balance, and this interaction is fundamental not only for their survival and development but also for ours. This is why it's so important to preserve that harmony, although nowadays it's being threatened by the direct action of human beings and global warming.

What is biodiversity?
What is biodiversity?
The United Nation's Convention on Biological Diversity defines biodiversity as “the variability among living organisms from all sources."
In other words, it refers to the wide variety of living things that inhabit our planet.
In 1992, the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED), also known as the "Earth Summit," was held in Río de Janeiro. Major agreements were reached at this meeting, such as the Climate Change Convention and the so-called Convention on Biological Diversity. The latter has three main goals: the conservation of biological diversity, the sustainable use of its components, and the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from genetic resources. Ratified by 196 countries, its aim is to promote measures for a sustainable future in which the conservation of biodiversity is a priority. Its signing on May 22, 1994, led the UN General Assembly to declare May 22 as the International Day for Biological Diversity.
Earth's species are not equally distributed around the globe. In fact, 10% of the planet's surface is home to 70% of its biodiversity. That's why its protection has become so essential in the so-called "mega-diverse countries," where biodiversity is more abundant. They total 17 and hold two thirds of all non-fish vertebrate species and three quarters of all higher plant species.
But, how can we find out how much biodiversity there is in one specific area? There are various indices, such as the Shannon–Wiener, that take into account the number of species and the relative abundance of each in a given area.
Types of biodiversity
Types of biodiversity
Importance of biodiversity
Importance of biodiversity
Biodiversity is fundamental for the planet. In fact, its loss has become the third most important risk worldwide in 2022, according to the World Economic Forum (WEF). Moreover, biological balance is necessary for diverse and crucial aspects such as health, nutrition, and safety, among others. For example, if coral reefs disappear, one fourth of marine species on the planet will also disappear. On top of that, the coast would lose its protection against the impact of waves and tsunamis. The same happens with forests, which regulate temperatures and climates while protecting the soil from erosion and serving as a refuge and food for many other species. In a nutshell, greater biodiversity offsets the vulnerability of ecosystems against major environmental changes.
There are different aspects in which care and preservation of biodiversity can have repercussions on both society and the environment. Here are three types:
- Economic aspect: Biodiversity is basic for everyday life. For example, it's required to provide us food and to manufacture pharmaceuticals. Likewise, an ecosystem rich in biodiversity attracts tourists, while allowing industry to extract different elements that enhance our development, among many other examples.
- Scientific aspect: Each species holds a piece of valuable information about its life and evolution. Additionally, it allows us to identify the role of each group in the ecosystem where it is found.
- Ecological aspect: The elements that make up the biodiversity of an area naturally regulate the flows of energy and material. For instance, biodiversity has an impact on aspects such air quality, water purification, pollination, and soil erosion control, among others.
Biodiversity, sustainable development, and climate change
Biodiversity, sustainable development, and climate change
Today, biodiversity is undermined by a range of factors including climate change, overexploitation of resources, introduction and subsequent proliferation of invasive species outside their usual habitat, and pollution, among others. For example, the change in how soil is used is one of the main factors for biodiversity loss. This is why it is fundamental to take action against these and other factors, known as drivers of change, with measures such as these:
- Avoid anything that incentivizes species extinction: e.g., poaching, overfishing, or widespread tree felling.
- Reduce consumption and contamination: If we reduce indiscriminate consumption, contamination will decrease, which is something that also occurs when we consume fair trade products or support local businesses. Incentivizing the circular economy can also allow us to optimize resources and promote the responsible consumption of raw materials.
- Protect species at risk: Both governments as well as other entities can take measures to protect endangered species in a certain ecosystems.
- Educate and spread awareness: It's crucial that society be aware of the importance of respecting biodiversity and how its actions can contribute to preserving or destroying it.
Repsol's biodiversity promotion projects
Repsol's biodiversity promotion projects



