Ecological footprint
Ecological footprint
A sustainability indicator to measure our environmental footprint.
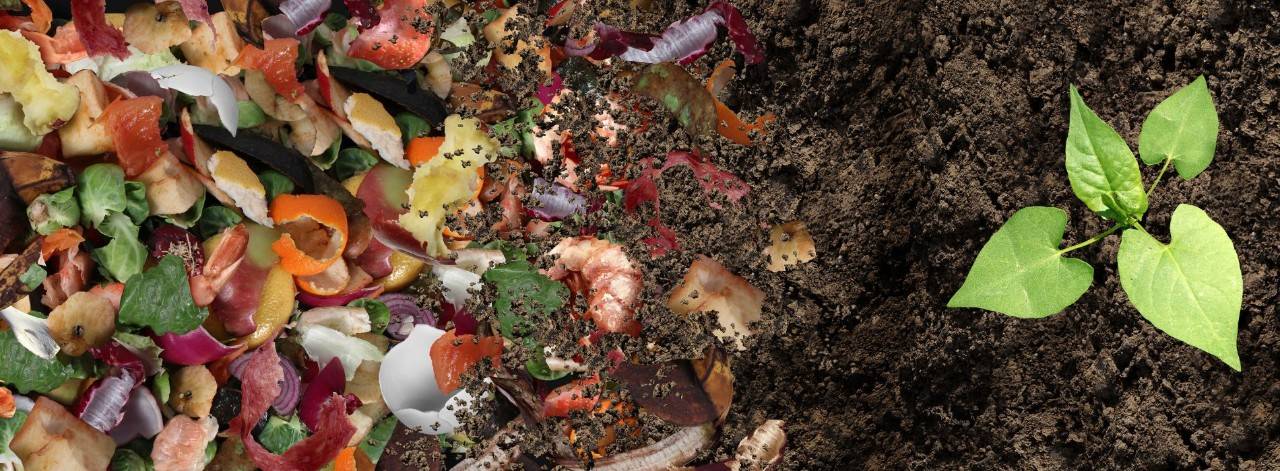

What is composting and what is it used for?
A natural fertilizer mitigating our ecological footprint
Recycling offers many alternatives to manage household organic waste more efficiently through techniques such as composting.
Biodegradable organic waste, also known as biowaste, represents approximately half of the content of the garbage bags generated every day in Spanish households. Thanks to composting, it's possible to recycle this waste to give it a new use or produce energy following the circular economy principles.
Optimization of waste management is at the heart of this new economic model, which is capable of combining efficiency and care for the environment. Within this cross-cutting strategy, composting is an excellent example of what we can do at an individual level to achieve this goal. In addition to recycling part of our household waste, this practice also enables us to reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills and mitigate our ecological footprint, which moves us towards a zero waste production model.

What is composting and what is it for?
Composting is a technique that results in the production of natural fertilizer produced from the decomposition of organic waste by bacteria, fungi, and animals such as worms, earthworms, and ants. This process also occurs in nature as a result of the biological oxidation of plant remains.
What kind of organic waste is used for composting? Most of the food waste we throw away every day can be composted: fruit and vegetable skins, fish bones, bones, egg shells, etc. Plant waste is also used such as pruning waste or smaller plant elements from gardening work. Used napkins and kitchen paper, sawdust, cork stoppers, and wood shavings are also suitable materials for this practice.
As a result, home composting will save your home or residential community money since you won't have to invest in fertilizers. At the environmental level, composting also brings important benefits, since by recycling organic waste, it reduces the amount of waste that goes to landfills or to final treatments such as incineration and, consequently, the emission of polluting gases such as methane and carbon dioxide.
Types of composting
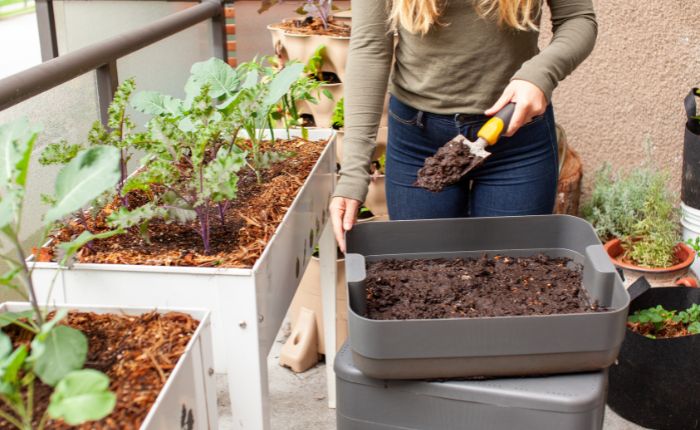

Traditional composting
This type of compost is made using organic waste that is left to rest in piles that are turned regularly, either manually or mechanically, to oxygenate the mixture and prevent the compost from compacting.
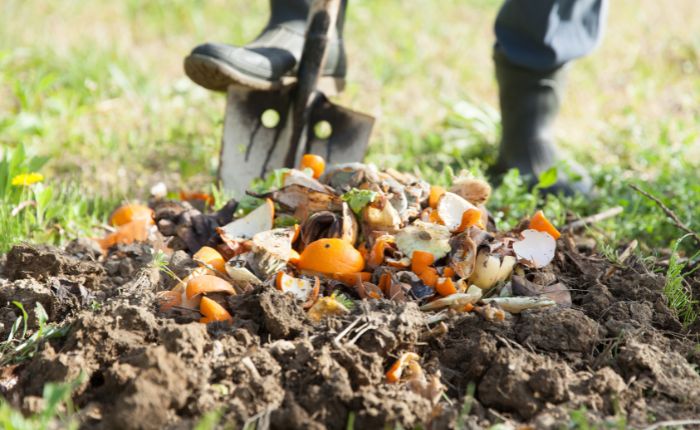

Surface composting
With this composting method , known as static pile composting, you simplify the aforementioned process by applying the organic matter directly onto the soil. In this way, as it decomposes, nutrients leak directly into the soil.
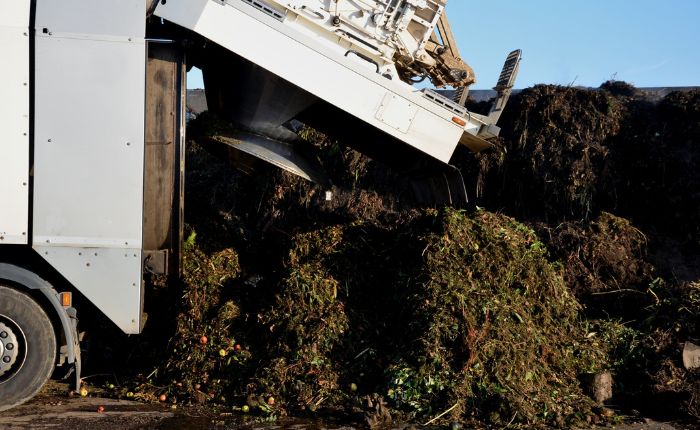

Industrial composting
This type requires more complex installations, including a forced ventilation system and temperature control to foster the development of more active bacteria that produce compost more quickly and avoid the appearance of germs.
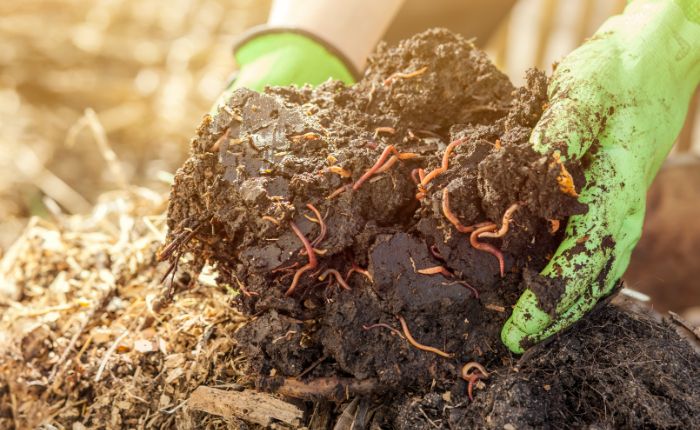

Vermicompost or earthworm humus
This composting technique uses California red worms, a species capable of devouring virtually any plant debris. The resulting compost, known as worm castings or vermicompost, is known for its high nutritional properties.

Manure composting and poultry composting
Originally from Japan, this type of compost makes use of the remains derived from rice cultivation, adding water, molasses, crushed charcoal, yeast, and other elements to accelerate the decomposition.
What is compost used for?
How to compost at home
As you will see below, composting at home is a really easy process to obtain a perfect natural fertilizer to take care of your plants or your community's gardens. Are you up for trying this technique of domestic recycling?
Ecological footprint
A sustainability indicator to measure our environmental footprint.

Biodiversidad
All about biodiversity. Do you know how many types there are?